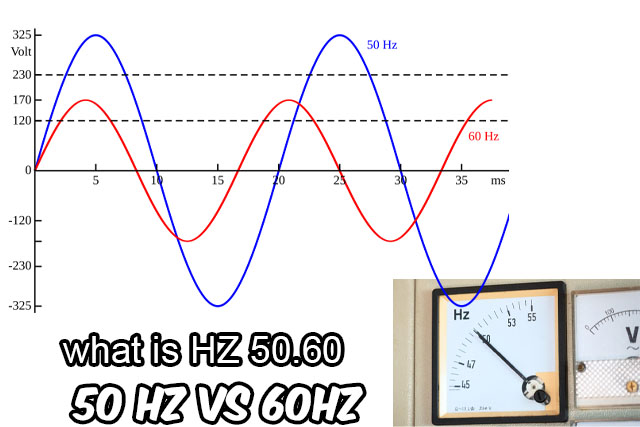
In the world of electrical systems, frequency plays a crucial role in determining how electrical power is distributed and utilized. Here, we will explore the concepts of 50Hz and 60Hz frequencies, explaining their significance and where they are commonly used.
What is Frequency?
Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), refers to the number of cycles per second in an alternating current (AC) signal. It dictates the rate at which the electrical current alternates direction. Different regions around the world use different frequencies, primarily 50Hz or 60Hz.
50Hz Frequency
- Definition: 50Hz means that the electrical current alternates direction 50 times per second.
- Usage: This frequency is predominantly used in most countries across Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia.
- Electrical Appliances: In regions where 50Hz is standard, electrical devices and appliances are designed to operate efficiently at this frequency.
60Hz Frequency
- Definition: 60Hz indicates that the electrical current alternates direction 60 times per second.
- Usage: This frequency is commonly used in North and South America, including countries such as the United States, Canada, and some parts of South America.
- Electrical Appliances: Devices and appliances in these regions are manufactured to function optimally at 60Hz.
Why the Difference?
The difference in frequency is a result of historical development and regional standards established early in the electrical industry. Each frequency has its advantages and is optimized for the electrical grid and power distribution systems of the respective regions.
Impact on Electrical Devices
- Compatibility: Appliances and devices are often designed to operate at a specific frequency. Using a device designed for 60Hz in a 50Hz region may cause performance issues or damage, and vice versa.
- Efficiency: Frequency affects the efficiency and operation of electrical equipment, including motors and transformers. Equipment designed for a particular frequency will generally perform best at that frequency.
Summary
Understanding the frequency of electrical systems—50Hz or 60Hz—is essential for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance of electrical devices and appliances. Different regions use different frequencies based on historical and technical standards, influencing how electrical power is utilized globally.
For more detailed information and resources, visit our website Watt Vission.